Understaing MVC for MERN stack
Admin
•
03-04-2023
•
# Tutorial
When it comes to developing a web application (or any type of software), having a well structured architecture and clean code is essential to ensuring maintainable, scalable and robust applications. Fortunately, many developers have devised architecture and design patterns that help achieve this goal.
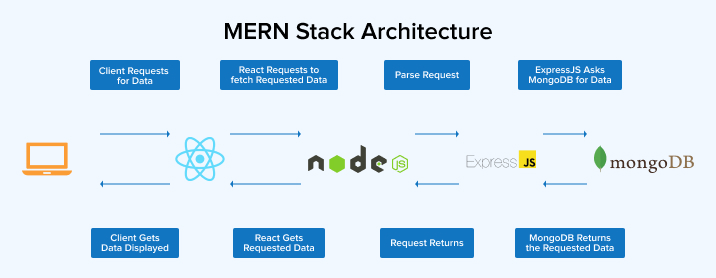
One of the most used architectural patterns in the industry is MVC, which stands for Model, View, Controller. It’s an architectural pattern that separates an application into three distinct components: the Model, the View, and the Controller
Model:
The model represents the data and business logic. In the MERN stack, the model is handled using MongoDB, a popular NoSQL document-based database. However, since MongoDB is schemaless, Mongoose, an object modeling library, is often used to create schemas and models. Mongoose allows developers to define the structure of the data and provides a straightforward way to interact with MongoDB
View:
The view is responsible for displaying the data to the user. In the MERN stack, this is done using React.js, a popular open-source Ui library developed by Facebook. React uses JSX (Javascript XML), a syntax extension that allows mixing HTML with JavaScript. JSX is used to describe the appearance and structure of the frontend of the application.
Controller:
The controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It receives requests from the view (typically in the form of, GET, POST, PATCH or DELETE requests) and updates both the View and Database accordingly. In the Mern stack, the controller is implemented using Express.js, a web application framework for Node.js. Express routes handle incoming requests and call the appropriate methods on the model to process data and respond to the client.
In addition to the above, in the MERN stack, it's also common practice to have a separate file to handle your routes. Routes designate which functions should be called in your controller file. For example, for the route 'api/user/login' we would call the function accountLogin and for the route 'api/user/signup' we would call the function accountSignup.
Folder structure

Above is an example of the proper folder structure for MVC using the MERN stack. Here, we have seprate folders for handling different functions of the backend. The client (Also know as the View or Frontend) is handled by a seperate folder outside the backend directory.
Server: The server (or sometimes referred to as the backend) is a directory used to represent the backend of an application. This typically includes the Express server setup, route definitions, controllers, models, and any other backend logic.
Client: The client or frontend is a directory used to represent the frontend of an application. The front end is responsible for the layout, and anything the user can see or interact with. In the MERN stack, the frontend is built using React.js.
Conclusion
The MVC architecture provides a well-structured way to develop applications in the MERN stack. By separating concerns into Models, Views, and Controllers, developers can ensure their applications are maintainable, scalable, and robust. This separation not only makes the codebase easier to manage but also facilitates a more effective and streamlined development process, allowing teams to work more efficiently. By following the MVC pattern, developers can create applications that are easier to debug, test, and extend, leading to higher-quality software and a better overall user experience



